Intimate Care School
The period
The vagina & vulva

The vagina
The vagina is the canal between the vaginal opening and the uterus. It is about 10 cm long and can expand and become longer when aroused or when giving birth. The muscles around the vagina are strong, you can feel it yourself if you insert a finger and squeeze. These muscles are like any other muscles, they get stronger the more they are exercised. The walls of the vagina are covered by a moist mucous membrane and when you get arroused, you get wetter than usual. This means that the friction is reduced when you masturbate or have sex, so that the vaginal wall is not damaged.
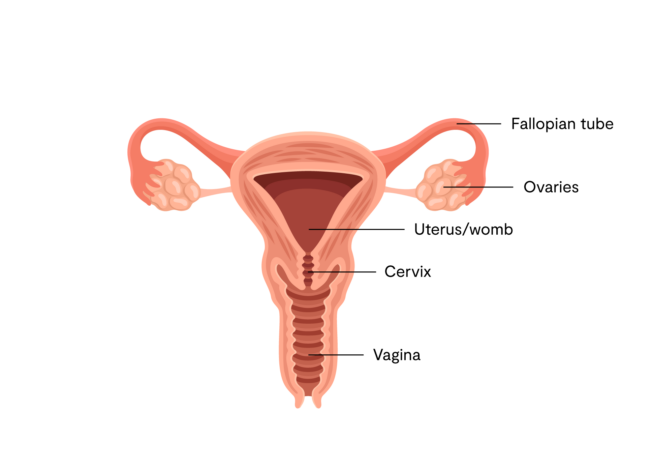
The cervix and the uterus
The cervix consists of glands that produce discharge and it is thanks to the discharge that the vagina keeps itself clean and moisturized. The cervix ends into the uterus, which is a cavity approximately the size of a chicken egg.
Fallopian tubes
On the upper part of the uterus is a tube on each side, which is the fallopian tubes. They each form an oval and at the end of the other side they meet the ovaries.
Ovaries
The ovaries are two to three centimeters in size and this is where the ovulation takes place. Ovulation is when an ovarian follicle burst in the ovaries and the mature egg slides down into the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized.
G-spot
The G-spot is not really a spot but an area that contains lots of nerve fibers. The area is located a bit into the vagina on the front wall of the vagina, ie towards the stomach. When aroused, the area becomes harder and swells. To stimulate the G-spot requires a stronger touch than when stimulating the clitoris.


